Clinical
Presentation
1. Uncontrolled HTN
despite multiple antihypertensive medications.
2. HTN in young women
and children.
3. Sudden onset of HTN.
4. Severe HTN after
age 55.
5. renal failure, when
treated with ACEI.
6. An abdominal
bruit.
7. Acute flash
pulmonary edema in absence of acute coronary events.
8. Uncontrolled HTN
and declining renal function.
DIFFERENTIAL
DIAGNOSIS
Essential hypertension and other causes of secondary hypertension
1. Essential HTN:
- Primary HTN is the major cause of HTN.
- absence of evidence of secondary causes.
- Investigate for specific secondary etiology to exclude.

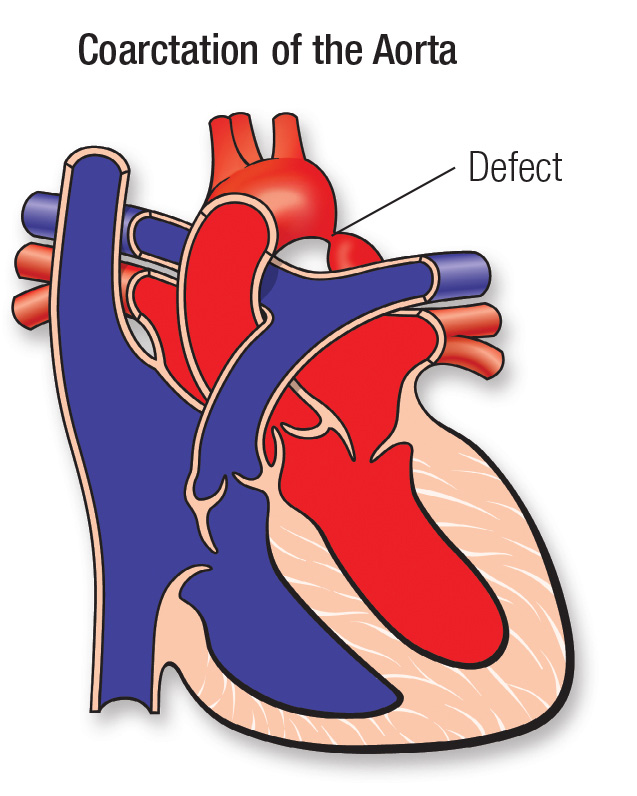
2. Coarctation of the aorta:
·
cause of HTN in children and young
adults.
·
young, pulse differential
between the brachial and femoral arteries, and a history of claudication.
3. Cushing
syndrome (Glucocorticoid excess):
- centripetal obesity, moon faces,
buffalo hump, and purple striae.
- Night salivary cortisol, urinary cortisol, and a low-dose dexamethasone suppression test.
4.
Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism:
- symptoms of thyroid hormone
deficiency or excess.
- TSH and free T4.
5. Oral
contraceptives or other medication-induced HTN:
- stop medications will normalize BP.
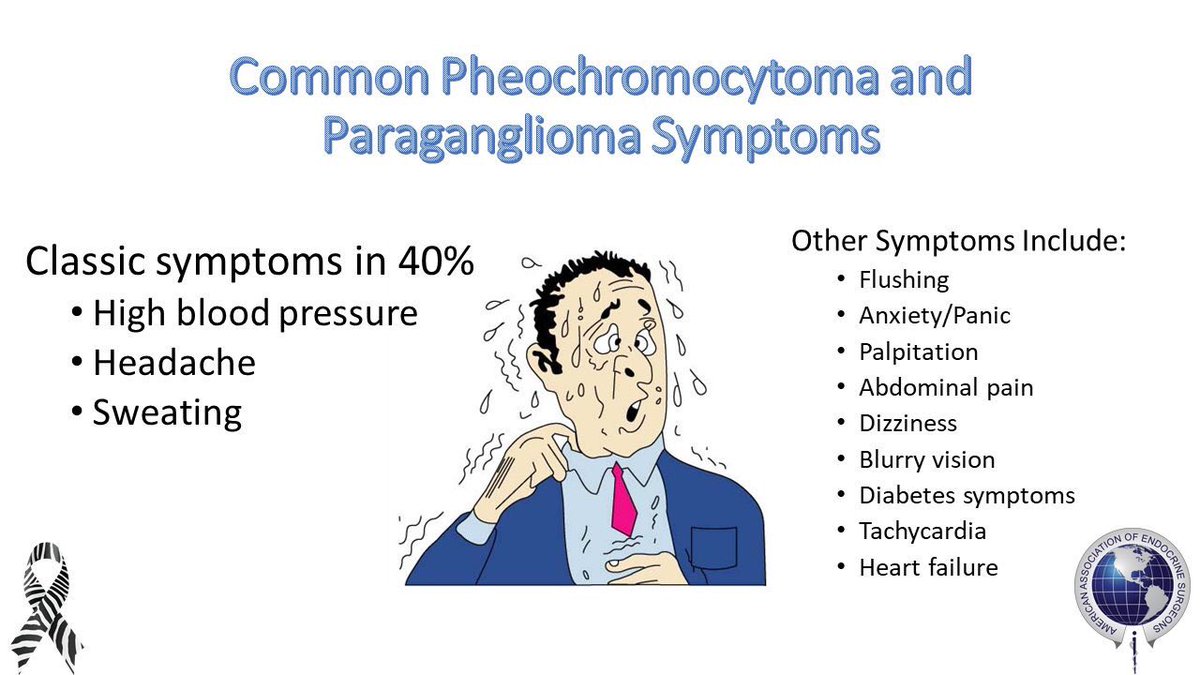
6.
Pheochromocytoma:
- episodes of
palpitations, diaphoresis, and severe headache.
- increase of plasma fractionated
metanephrines, urinary metanephrines, or urinary catecholamines.
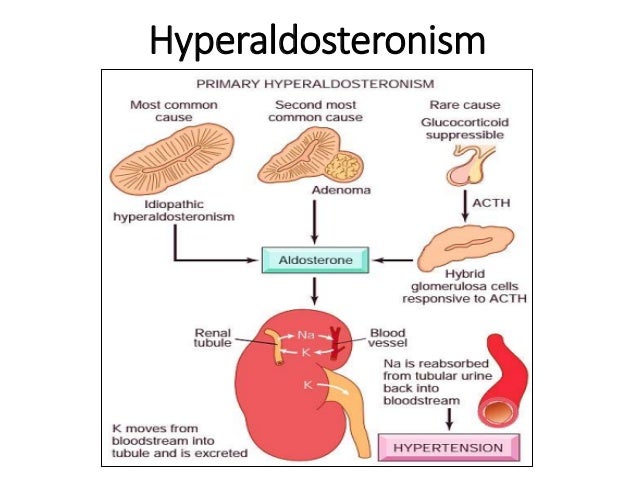
7. Primary
aldosteronism:
- ↑ plasma aldosterone and ↓ plasma
renin activity.
- CT/MRI and renal vein sampling can
localize the source and differentiate between adrenal adenoma and
adrenal hyperplasia.
8. Primary
hyperparathyroidism:
- Hypercalcemia, mood disturbances, and history of kidney stones.
9. Primary
kidney (Parenchymal) disease:
- difficult to differentiate
from RVH, but the absence of renovascular disease,
elevated creatinine, abnormal urinalysis,
- imaging: renal parenchymal
disease.
10. Obstructive
sleep apnea: snoring at night and fatigue during the day. Usually obese.