Lab
1. Cr, BUN, Na, K,
bicarbonate, and chloride.
- RAS → renal hypoperfusion and
impaired renal function.
- renal impairment will affect
choice of imaging and treatment.
2. Peripheral plasma
renin activity (PRA): not much useful.
- Not accurate: Normal in many RVH pts
and ↑ in many essential HTN pts.
- needs strictly conditions
(salt and water restriction, stop antihypertensives).
3. Plasma aldosterone:
diagnose aldosteronoma (D.D.).
4. Plasma or urine
metanephrines: diagnose pheochromocytoma (D.D.).
Radiology
1. Duplex US
primary method of screening for RAS
Ø peak
systolic velocity (PSV) of RA assess degree of stenosis. PSV > 180cm/sec = significant RAS.
Ø measure
both the kidney length and resistive index (RI).
RI > 0.8 or renal length < 7 cm: significant intrarenal disease not corrected by renal revascularization.
adv:Ø safe
and accurate.
Ø sensitivity
and specificity >90%.
Ø avoids
exposure to nephrotoxic CM and ionizing radiation.
Ø difficulty
imaging the RA in obese patients
Ø less
anatomic detail for surgical planning than CTA or MRA.
2. CTA
Ø noninvasive
and widely available
Ø Sensitivity
and specificity >90%.
Ø accurate diagnosis
of RAS
Ø 3-D
reconstruction of the arterial anatomy, before revascularization.
Ø imaging
of the intraabdominal organs: detect other renal disease and assess other
etiologies of HTN (i.e., functional adrenal adenoma).
Ø nephrotoxic
CM and ionizing radiation.
3. MRA

Adv: (as CTA+)
Ø higher
sensitivity and specificity for RAS,
Ø 3-D reconstruction
of the arterial anatomy,
Ø imaging
of the kidneys and other abdominal organs.
Ø no risks
of ionizing radiation or contrast-induced nephropathy.
Ø Gadolinium
is contraindicated in severe renal impairment (GFR < 30mL/min) due to the
risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF).
Ø claustrophobia
Ø metal
implants → risk of moving with the magnetic field or will limit the image
quality (because of artifact).
4. Angiography
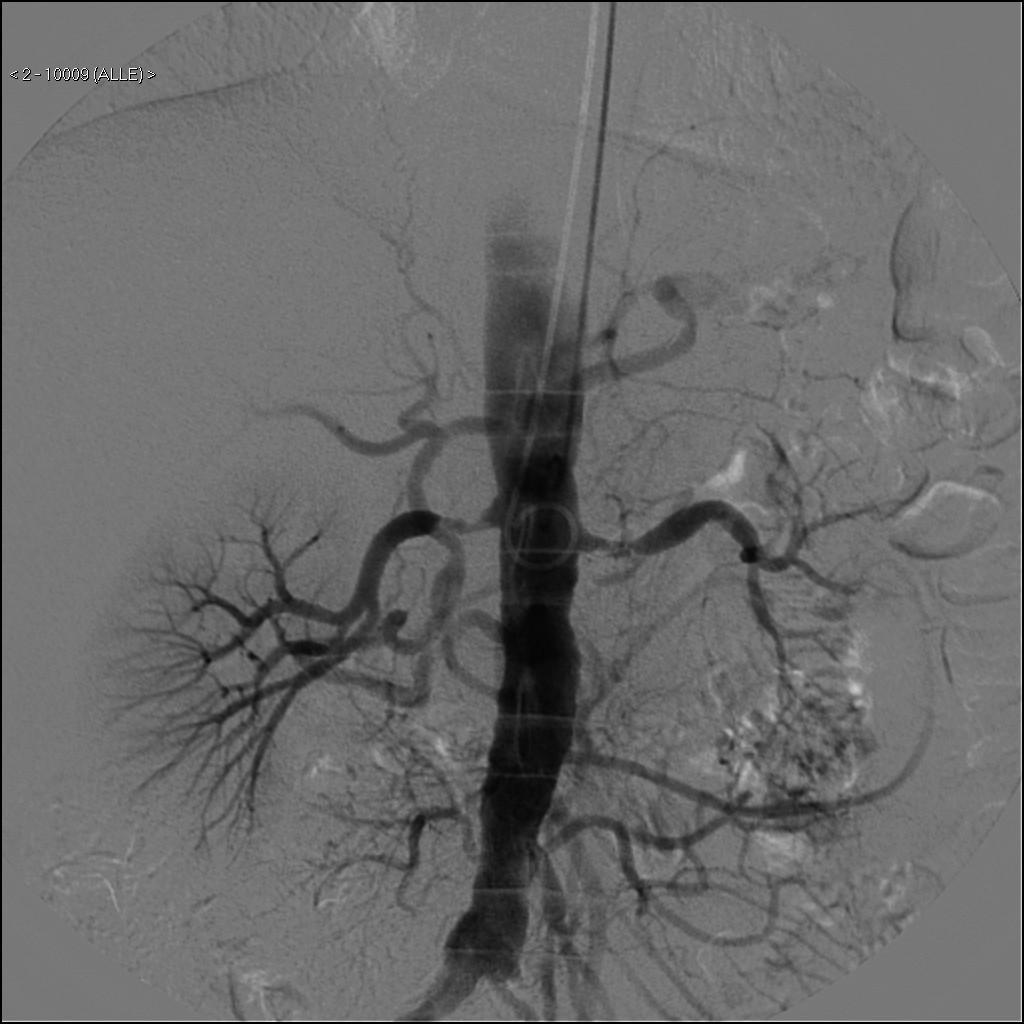
Still the gold standard for diagnosis of RAS. but Invasive.
Technique:
Ø Arterial
sheath access, usually either the common femoral artery or left brachial
artery.
Ø A
catheter is then positioned in the aorta at the level of the renal
arteries.
- Conventional
angiography.
- Digital
subtraction angiography (DSA): fluoroscopy machine provides high
quality images of aorta and RA (gold standard for diagnosing RAS).
- superselective
angiography: RA and segmental branches
- pressure
transduction across a visualized lesion.
Ø Diagnosis
RAS
Ø Therapeutic
(if a lesion is identified, it can be treated same time).
Ø arterial
access complications: thrombosis or pseudoaneurysm formation at the sheath
site, dissection of the access vessels, and embolism (including embolic
stroke if the brachial approach is utilized).
Ø Contrast
induced nephropathy: CO2 can be used instead of CM.
Functional studies
RAS alone does not make the diagnosis of RVH.functional tests: to determine if RAS is the cause of HTN
1. Renal radionuclide
scan (Radionuclide renography)
Ø measure
split renal function.
Ø abnormal
uptake and excretion of affected side (in severe RAS).
Ø follow
up of renal function.
Captopril renography: Renography after ACEI.
Ø diagnose
RVH more accurately as renography may be normal with RAS (due to
compensatory V.C. of the efferent arterioles).
Ø ACEI
blocks the angiotensin II-mediated efferent arteriole V.C., → block the
kidney’s natural compensatory mechanism → ↓ radioisotope uptake and
excretion by the kidney.
- Normal test excludes RVH.
- +ve test = renal etiology for HTN (RAS or
parenchymal disease) high false +ve.
2. Renal vein (RV) renin

value: determine if unilateral RAS is associated with increased renin from ipsilateral kidney.
Technique:
Ø stop
antihypertensive and Na restricted before study.
Ø renal
veins (RV) and IVC are catheterized percutaneously.
Ø RV
renin (bilateral) and IVC rennin measured.
Ø RV
renin/IVC renin ratio >1.5 (from same side of RAS) is +ve.






